Optimizing tree-based algorithms for student dropout prediction: a comparative study
Keywords:
Dropout Prediction, Tree-Based Algorithms, Machine Learning, Optimization Techniques, Dragonfly Workflow.Abstract
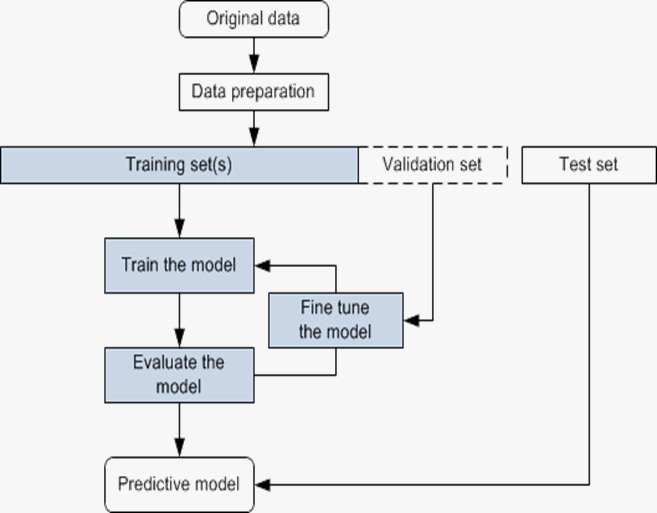
This study aims to predict student dropout by experimenting with different tree-based algorithms and optimization techniques. The goal is to improve prediction accuracy and support early intervention strategies in education. Applying the Dragonfly workflow, a structured and rigorous approach in machine learning. A range of tree-based algorithms including Decision Tree, Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, Extra Trees, Histogram-Based Gradient Boosting, Cat Boost, XG Boost, and Light GBM are evaluated. Optimizing its performance by hyperparameter tuning and cross-validation is conducted using Randomized Search CV, Grid Search CV, and Bayes Search CV. Among all algorithms, XG Boost consistently showed a high accuracy and slightly improved with BayesSearchCV. The Hist Gradient Boosting achieved the highest score overall under BayesSearchCV. It achieved the goal of building a robust predictive framework by combining EDA with tree-based algorithms. Key models were optimized and the Bayes Search CV showing the most consistent performance, particularly for XGBoost and HistGradient Boosting that highlighting the value of effective tuning for accurate student dropout prediction. Future work should begin with structured EDA and prioritize tree-based models for high performance. The BayesSearchCV is recommended as a standard approach to improve model effectiveness across domains.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Roman B. Villones

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




