Fault Identification and Protection of Induction Motor Using PLC and SCADA
Keywords:
Overload, Over Voltage, Under Speed, Thermal Overload.Abstract
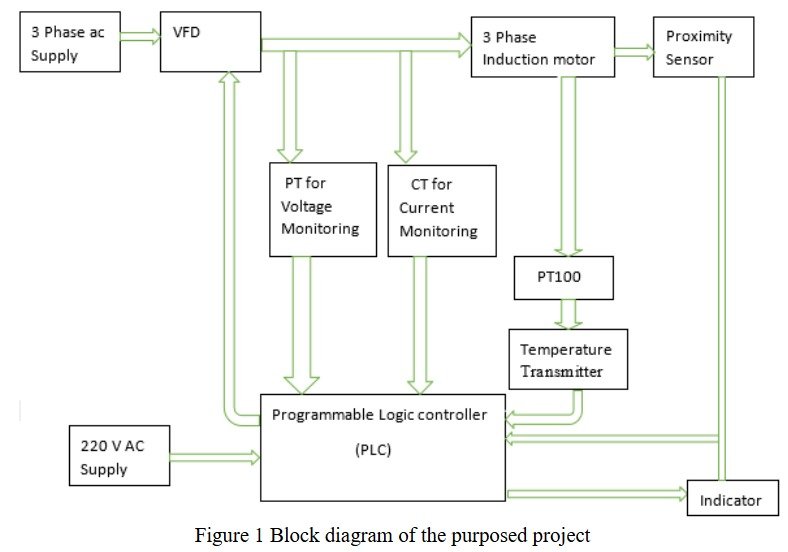
If not properly maintained, AC induction motors are prone to malfunction. A protective system is put in place to keep an eye on the motor's performance under both normal and trip conditions to remedy this. The system may either modify the input voltage and current to restore normal performance in the event of faults like stator, rotor, bearing, or eccentricity issues or shut down the motor before irreparable harm is done. This guards against sudden shutdowns that could endanger employees, prevents unexpected motor failure, and reduces unforeseen costs. Due to their extensive industrial use, protecting induction motors from overvoltage, overcurrent, under-speed, and overheating is essential. Voltage and current relays, timers, contractors, and other traditional protection techniques are mechanical devices. Both computer-based and PIC-based techniques have fewer mechanical components, although the former needs analog-to-digital conversion cards while the latter does not display the observed electrical parameters. In this work, a PLC based protection technique that does away with contractors, relays, and conversion cards is presented. It keeps an eye on system errors, motor voltages, currents, speed, and temperature while showing alerts on a computer screen. In comparison to conventional, computer, and PIC-based systems, experimental findings show that this PLC-based approach is more precise, efficient, and offers a safer and more visible environment.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Nigam Bam Malla, Ajay KC

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




