Effect of Calcium Nitrate and Calcium Carbonate on Plant Growth, Fruit Quality and Yield of Papaya Cv. Red Lady
Keywords:
Foliar, Growth, Papaya, Quality, Yield.Abstract
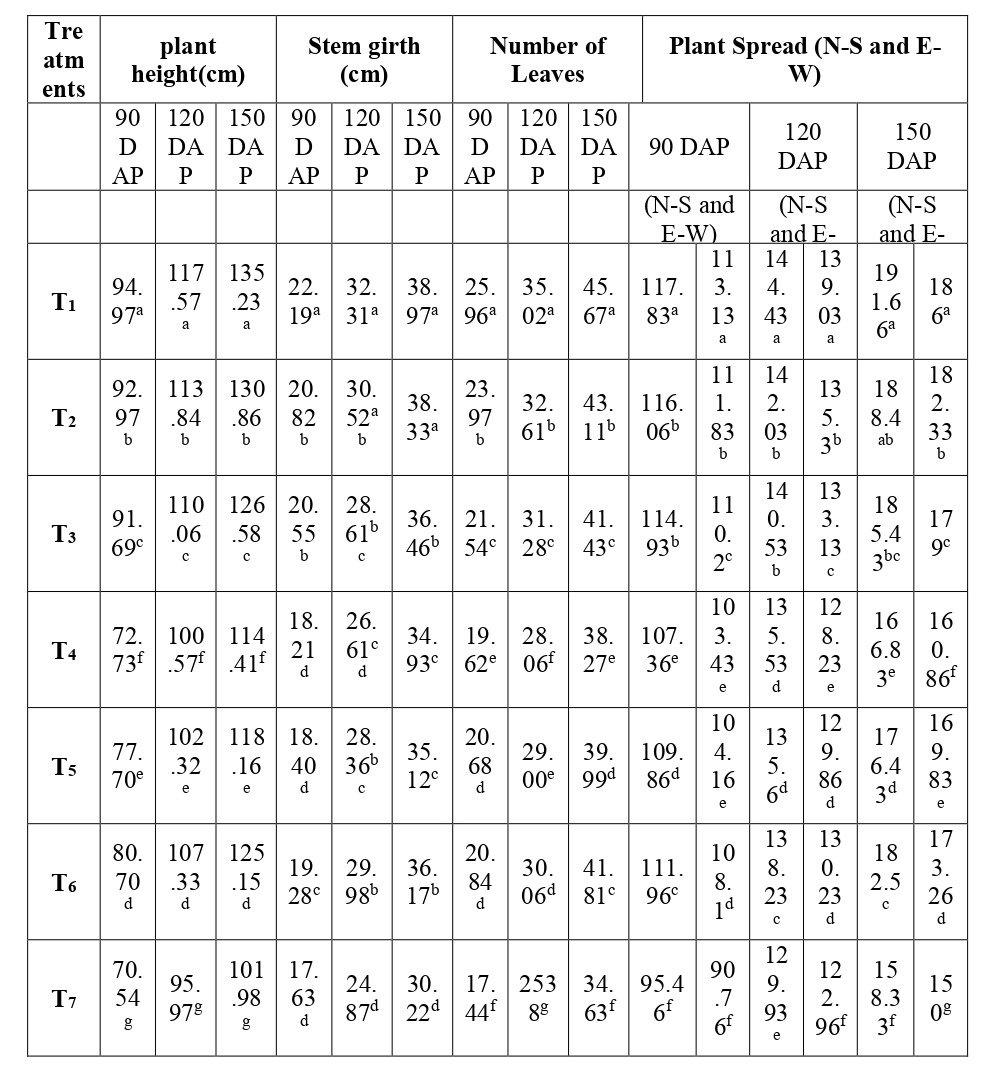
A field experiment was performed to study the effects of foliar applications of CaCO3 and Ca(NO3)2 on growth, quality, yield, and shelf life of papaya (Carica papaya) Cv. Red lady. Calcium (Ca) is one of the major plant nutrients which affects significantly the formation of the cell walls and cell membranes and also enables the production of biomass with proper plant growth and function. In the current experiment, papaya seedlings were well established in the orchard, well-irrigated with standardized nutrient solutions with all required inter-culture activities. Four different pre-harvest foliar application sprays were provided with two varying sources of Ca (CaCO3 and Ca(NO3)2) at three concentrations of each with CaCO3 (2%, 1%, 0.5%) Ca(NO3)2 (2%, 3%, 4%) at different stages of growth like flowering stage, fruit set stage, pre-harvest stage. The study revealed that foliar spray of above mentioned concentrations showed a profound improvement in vegetative growth of plants in terms of their height and diameter as compared to the plants in control treatment and also affected the fruit quality of papaya fruit.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




