DPPH Screening in Mentha and Guggul Plant Different Extract
Keywords:
Herbal plant, Mentha, Guggul, Antioxidant, Solvent, DPPHAbstract
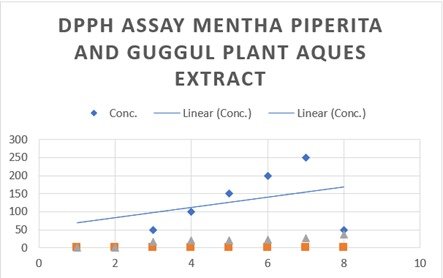
Free radicals are extremely reactive atoms or molecules that have one or more unpaired electrons on their outer orbital and have the potential to harm biological cells. The human body naturally creates antioxidants to combat free radicals, but because oxidative stress and aging cause more free radicals to develop, an exogenous antioxidant is required. The Plantae family has a lot of potential as a source of exogenous antioxidants because it is the largest family in the plant world. The goal of this study was to ascertain the antioxidant properties of the aqueous and ethanol extracts of mentha and guggul leaves, respectively. The DPPH technique was used to measure antioxidant activity, and the findings were noted for further study.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
